DEPTH Blog
Nitrox Breathing Mixtures
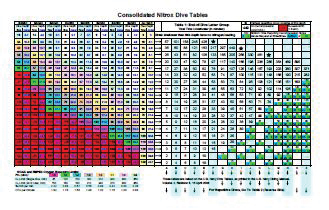
Divers have used air as a breathing gas since the beginning of diving. Its principal advantages are that it is readily available and inexpensive to compress into cylinders or use directly from compressors with surface-supplied diving equipment. Air is not the “ideal” breathing mixture for diving because of the decompression liability it imposes. Since decompression obligation is dependent on exposure to inspired PN2 (nitrogen partial pressure), this obligation can be reduced by replacing a portion of the nitrogen content of the diver’s breathing gas with oxygen, which is metabolized by the body. This is the fundamental benefit of enriched air nitrox (Nx) diving (Wells 1989). Historically, the two most commonly used nitrox mixtures in NOAA have been 32% and 36% oxygen. Once called NOAA Nitrox 32 (NN32) and NOAA Nitrox 36 (NN36), such mixtures are now identified using a more general nomenclature as Nx32 and Nx36. The remaining gas in nitrox mixes is considered to be nitrogen, even though it may contain other inert gases like argon. “Nitrox” is a generic term that can be used for any gaseous mixture of nitrogen and oxygen, but in the context of this chapter, the implication is that nitrox is a mixture with a higher concentration of oxygen than that of air. Using such oxygen enhanced mixtures can significantly increase the amount of time a diver can spend at depth without incurring additional decompression when compared to air diving.
Tables are not the only way to determine no-decompression limits when using nitrox. Other methods may provide increased bottom times. For example, a diver making a 92 fsw (28.2 msw) dive using one of these mixtures can increase the air no-stop dive time from 25 minutes to as much as 48 minutes based on using EAD (equivalent air depth) computations. Assuming a diver uses a 30 fpm (9.2mpm) rate of descent, a diver using air will have only 22 minutes on the bottom, whereas the diver breathing Nx36 will have 45 minutes. This is a 104% increase in bottom time. The increased bottom time does not come without an operational price tag. Nitrox diving comes with limits and safety procedures. This chapter explains why nitrox works and describes how NOAA divers take advantage of these gases for their scientific underwater work.
(Source: NOAA Diving Manual: Diving for Science and Technology, 5th Edition; 2013)
SUGGESTED READING AND RESOURCES
When you subscribe to the blog, we will send you an e-mail when there are new updates on the site so you wouldn't miss them.